Linear Models
1 Linear Regression
1.1 Imports
import matplotlib.pyplot as pyplot import pandas import seaborn from sklearn.linear_model import ( Lasso, LinearRegression, Ridge, ) from sklearn.datasets import load_boston from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
%matplotlib inline seaborn.set_style("whitegrid")
1.2 The Data
This is the same data I used for k-nearest neighbors regression.
boston = load_boston() print("Boston data-shape: {0}".format(boston.data.shape))
Boston data-shape: (506, 13)
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(boston.data, boston.target)
1.3 The Model
model = LinearRegression() model.fit(X_train, y_train)
print("coefficients: {0}".format(model.coef_)) print("intercept: {0}".format(model.intercept_))
coefficients: [ -5.29188465e-02 3.27516047e-02 5.15495287e-02 1.96191849e+00 -1.70355026e+01 4.26984342e+00 -4.66261395e-03 -1.24731581e+00 2.40316945e-01 -1.12757320e-02 -9.67653044e-01 1.07129222e-02 -4.58665079e-01] intercept: 31.315219281412134
pollution_index = 4 names = ["Crime", "Large Lots", "Non-Retail Businesses", "Charles River adjacent", "Nitric Oxide", "Rooms", "Old Homes", "Distance to Employment", "Access to Highways", "Tax Rate", "Pupil-Teacher Ratio", "Blacks", "Lower Status"] pandas.Series(model.coef_, index=names)
Crime -0.052919 Large Lots 0.032752 Non-Retail Businesses 0.051550 Charles River adjacent 1.961918 Nitric Oxide -17.035503 Rooms 4.269843 Old Homes -0.004663 Distance to Employment -1.247316 Access to Highways 0.240317 Tax Rate -0.011276 Pupil-Teacher Ratio -0.967653 Blacks 0.010713 Lower Status -0.458665 dtype: float64
The price of homes in Boston is negatively correlated with Crime, Nitric Oxide (pollution), Distance to employment centes, Tax Rate, Pupil:Teacher ratio and the Lower status of the residents, with pollution being the overall largest factor (positive or negative). The most positive factors were the number of rooms the house had and whether the house was adjacent to the Charles River.
print("Training r2: {:.2f}".format(model.score(X_train, y_train))) print("Testing r2: {0:.2f}".format(model.score(X_test, y_test)))
Training r2: 0.74 Testing r2: 0.73
The training and testing scores were oddly close, suggesting that this model generalizes well.
training = pandas.DataFrame(X_train, columns=names)
seaborn.pairplot(training)
2 Ridge Regression
This model uses L2 regression to reduce the size of the coefficients.
ridge = Ridge() ridge.fit(X_train, y_train)
print("Training r2: {0:.2f}".format(ridge.score(X_train, y_train))) print("Testing r2: {:.2f}".format(ridge.score(X_test, y_test)))
Training r2: 0.74 Testing r2: 0.72
This time the testing did a little worse than without ridge regression.
pandas.Series(ridge.coef_, index=names)
Crime -0.048337 Large Lots 0.032897 Non-Retail Businesses 0.016831 Charles River adjacent 1.789245 Nitric Oxide -8.860668 Rooms 4.270665 Old Homes -0.011137 Distance to Employment -1.125192 Access to Highways 0.224993 Tax Rate -0.012211 Pupil-Teacher Ratio -0.891977 Blacks 0.010977 Lower Status -0.471429 dtype: float64
Once again pollution and the number of rooms a home had were the biggest influence on the price of the home.
3 Lasso Regression
This model uses L1 regression to remove the variables that don't influenc the outcome.
lasso = Lasso() lasso.fit(X_train, y_train)
print("Training r2: {0:.2f}".format(lasso.score(X_train, y_train))) print("Testing r2: {0:.2f}".format(lasso.score(X_test, y_test)))
Training r2: 0.67 Testing r2: 0.64
The Lasso did worse than the Ridge and ordinary-least-squares models did.
coefficients = pandas.Series(lasso.coef_, index=names) coefficients[coefficients==0]
Non-Retail Businesses -0.0 Charles River adjacent 0.0 Nitric Oxide -0.0 dtype: float64
The Lasso removed Non-Retail Businesses, Charles River adjacency, and pollution, even though the other models decided that pollution was the most important factor.
We can try and do better by using a less aggressive alpha value.
lasso = Lasso(alpha=0.01) lasso.fit(X_train, y_train) print("Training r2: {0:.2f}".format(lasso.score(X_train, y_train))) print("Testing r2: {0:.2f}".format(lasso.score(X_test, y_test))) coefficients = pandas.Series(lasso.coef_, index=names) print(coefficients[coefficients==0])
Training r2: 0.74 Testing r2: 0.73 Series([], dtype: float64)
Tuning the alpha can make it perform slightly better than the Ridge regression, but in this case making it aggressive enough to get rid of a column ("Nitric Oxide") makes it perform slightl worse than Ride regression.
training = pandas.DataFrame(X_train, columns=names) training["price"] = y_train seaborn.regplot(x="Nitric Oxide", y="price", data=training) pyplot.xlabel("Nitric Oxide") pyplot.ylabel("House Price") pyplot.title("Pollution vs House Price")
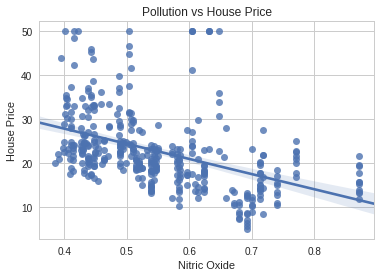
It appears that there is a linear relationship (although there are what appears to be some outliers).